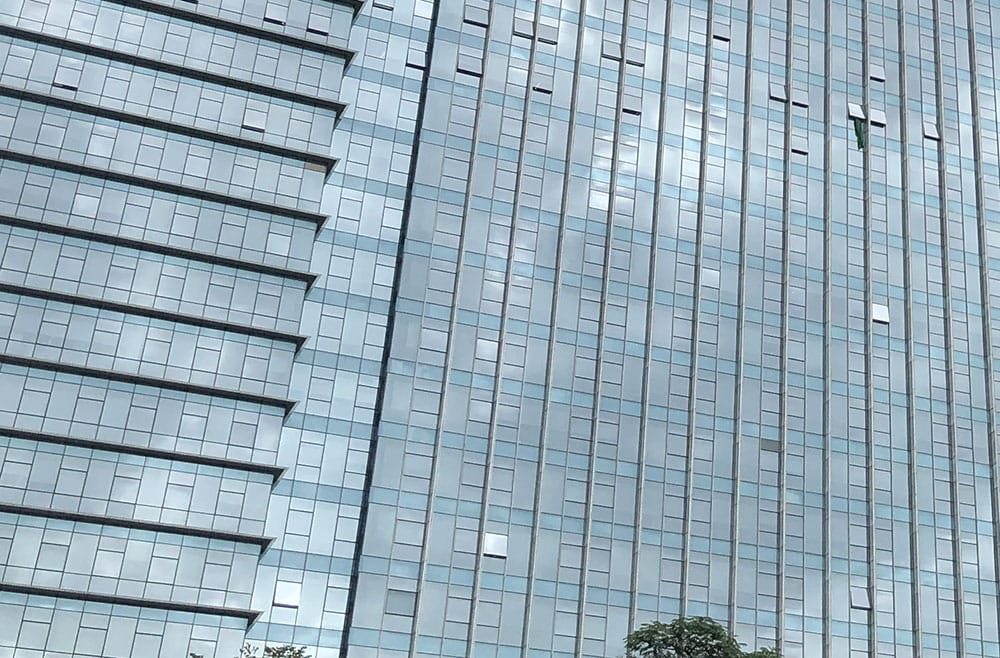
Glass curtain walls can be seen everywhere in buildings. Glass curtain walls have good visual effects and functional practicality. Glass curtain walls are composed of multiple precisely matched components to achieve their functions (enclosure, lighting, beauty) and safety. So what are the components of glass curtain walls? Zhongdong Curtain Wall will take you to have a look!

1. Glass panels of glass curtain walls:
This is the most core and visible part of glass curtain walls. According to design requirements, a variety of glass can be selected:
Single-layer glass: tempered glass (safety), semi-tempered glass, wired glass, etc.
Insulating glass: A combination of two or more pieces of glass, with dry air or inert gas (such as argon, krypton) filled in the middle, with excellent heat insulation and sound insulation performance. It is the current mainstream choice.
Laminated glass: PVB or SGP film is sandwiched between two pieces of glass. When broken, the fragments adhere to the film. It has extremely high safety and anti-fall performance, and also provides a certain sound insulation effect.
Low-E glass: The surface is coated with a low-emissivity film, which can effectively reflect infrared rays and significantly reduce heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter.
Enamel glass/screen-printed glass: Used for decoration or sunshade.
Glass is usually tempered or semi-tempered to improve strength and safety performance.
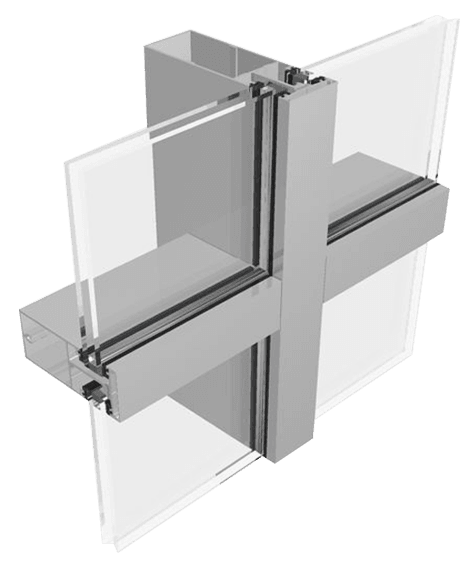
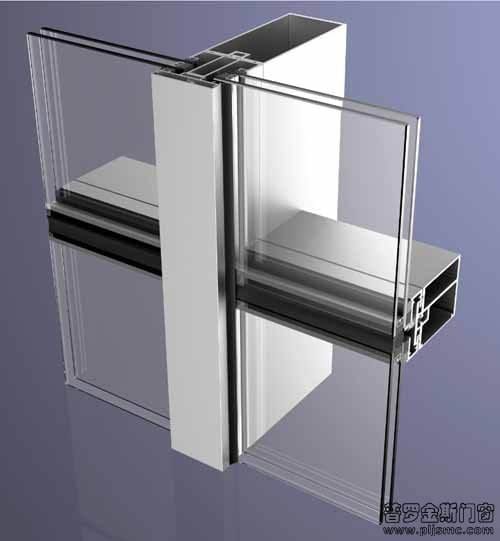
2. Support structure (frame system):
This is the “skeleton” of the curtain wall, responsible for bearing and transmitting the self-weight, wind load, earthquake load, etc. of the glass to the main structure.
Main components:
Column: Vertical component, which is the main load-bearing component and is usually fixed to the main structure (floor or beam).
Beam: Horizontal component, connected between columns, supporting glass panels.
Material: The most commonly used is aluminum alloy profile (light weight, good strength, corrosion resistance, easy processing and molding). In large or super-high curtain walls, steel structures (steel square tubes, I-beams, steel tube trusses, etc.) may also be used.
3. Connection and fixing system:
The glass panel is safely and reliably fixed to the supporting frame. Exposed frame curtain wall:
Press plate: Metal component pressed on the edge of the glass panel.
Buckle cover: Decorative cover plate, covering the screws of the press plate, providing an aesthetically pleasing surface.
Glue strip: Located between the glass, frame and press plate, it plays an elastic supporting, sealing and buffering role (such as EPDM).